Computer integrated manufacturing systems (cims) organically combine all aspects of the production process into a complete system. This requires that the design and process planning of the parts must have good feature integration and smooth flow of information during the product design process. . The integrated cad/capp system is based on the design concept of concurrent engineering, and encapsulates the design features and manufacturing features of the parts. Based on feature modeling in the design stage, the product design information generated by the cad system is automatically inherited during process planning, and processed. Corresponding to the method, the NC program required for the cam and the production management data required to provide the mis are generated. The parts can be processed and transmitted in the whole computer integrated manufacturing process without any resistance [1]. 1 Feature-based modeling 1.1 Feature definition classification As two stages of the design process, cad and camera have different meanings and expressions for the features of the parts. The design features of the parts mainly refer to the shape features, and the manufacturing feature information includes the process characteristics. Considering the needs of system integration, the shape is adopted. Feature-based multi-level description method. The difference between design features and manufacturing features is limited to the category of engineering semantics, and is expressed by feature classification, feature parameters and feature-specific surface features. According to this idea, The feature is defined as: one or more geometric shapes that are meaningful for design and manufacture, and can be composed of a basic cutting process to achieve uniformity of design features and manufacturing features. According to the above definition, the features of the part can be divided into main features and auxiliary features. The main features mainly describe the basic geometry and shape features of the inner and outer surfaces of the part, and the auxiliary features describe the secondary geometry of the part and its function, structure and process. There are characteristics of the combination requirements in the characteristics, and the auxiliary features are attached to the main features. 1.2 graphics database For the shaft parts, according to the geometric characteristics of the shaft parts, they are decomposed into different shaft sections. The shaft sections are divided into the main, auxiliary and surface elements of the parts. On this basis, the graphic database is established. The establishment can be carried out in the following two ways, each method corresponding to different cad modeling methods. 1) Graphic database based on parameter drawing The essence of the graphic database is the feature database containing the parameterized drawing program of the axis segment and the feature information field. Each record in the database contains the process characteristic variables of the geometric features of the axis segment, and correspondingly corresponding Parametric drawing program. Using the programming environment au-tolisp and objectarx in autocad2000 to write a parametric drawing program and associate it with the external database through ase and asi. When drawing, the corresponding drawing is extracted from the database while calling the drawing program according to the parameters. The process information is packaged and saved with the graphic geometry and saved to the external file. It is characterized by mature technology, easy operation, compact library structure and orderly information transmission, which is conducive to information feedback. However, it is difficult to add and modify the graphic database. Must be familiar with auto-cad programming. 2) Graphics database based on size-driven technology This form of database does not contain drawing programs, but saves basic graphics along with geometric parameters and feature variables in an external database. When drawing, use the size driver to pass geometric parameters. Change the shape of the graphic, and then output the process feature information to the external file. The advantage is that it is easy to add new axis data records in the database, and the modification is easy. However, the dynamic database must be used. 1.3 Feature Description and Modeling Process The feature information includes: 1) feature identification information, that is, a feature name and a feature identification number; 2) shape feature information, the shape has a characteristic implicit representation of the shape parameter, the structural parameter, the position parameter, and the face set explicitly represented by the feature; 3) the size And tolerance information, ie shaping dimensions, positioning dimensions, dimensional tolerances and geometric tolerances; 4) surface quality requirements information. The data structure of the features is as follows: Serial number main feature code (<Shaping size and tolerance> [Surface roughness] [Shape tolerance] [Position tolerance] [Positioning size and others] ([{Secondary feature code <Fixed size and tolerance> [Surface roughness] [Shape tolerance] [Position tolerance] [Positioning size and others]}]) With the feature information described by the above method, the next step is to model. The process of drawing the working diagram of the axis part in cad comes down to the process of feature modeling. Here, the segmentation modeling method is used to generate the part work drawing. The specific steps are: in the customized graphical menu, select the corresponding icon according to different shape features, then pop up the feature parameter dialog box under the icon for human-computer interaction input, and then by the drawing module (parameter drawing program or size) The driver draws the drawing and makes the necessary annotations, and adds all the information to the external data file. We call this file a graphic feature file. Thus, each part drawing corresponds to a specific feature file, and the drawing Each of the axis segments corresponds to a record in the signature file. When the axis segment is modified, the corresponding record in the file is also changed. 2 capp system reorganization of cad system information The information generated by the shaft parts in the cad process, in addition to the segmented feature information, also includes partial overall information, such as heat treatment requirements, hardness requirements, etc. in the technical requirements. The capp system requires a complete description of all the information involved. For this reason, the information generated in cad is divided into three categories, and the three-layer structure is used to express the part information, that is, the part layer, the feature layer and the geometric layer. The part layer includes the part name, the figure number, the material grade, the blank type, and the heat treatment method. And feature table; the feature layer includes feature name, feature code, shape feature parameter, size and tolerance, geometric tolerance, surface roughness and positioning size; geometric layer mainly refers to the underlying geometric information that is not tightly related to the processing. Using the knowledge base and inference engine of capp, automatically generate the steps/processes of the parts, select the processing equipment, arrange the processing sequence, select the tool and determine the cutting amount, and finally compile the process file, as shown in the figure below. 3 Conclusion The advantages of the cad/capp integrated system are as follows: 1) At the beginning of the design of the part, the processing elements of the part are comprehensively considered, which meets the requirements of parallel engineering design. It avoids the repeated input of information and improves the design quality and processability of the parts. 2) After unifying the design features and manufacturing feature definitions, it is easy to carry out joint design in the enterprise intranet to improve the efficiency of design. Further, the internet network can be used to realize remote collaborative design. 3) To lay the foundation for the integration of cad/cam in cims.
LED Wall washer :Let the light wash over the wall like water, mainly used for building decoration lighting, but also used to outline the outline of large buildings! Because LED has energy saving, high light efficiency, rich color, long life and other characteristics, so widely used!
Therefore, wall washing lamps of other light sources are gradually replaced by LED wall washing lamps. The technical parameters of LED wall washing lamps are roughly similar to that of LED projection lamps.
RGBW Wall Washer,Led Wall Washer RGBW,RGBW Wall Wash Lighting,RGBW Wall Washer Led Lights Jilin Province Wanhe light Co.,Ltd , https://www.wanhelight.com
In the traditional computer-aided design mode, the cad system pays attention to the mechanical properties and geometric modeling methods of the product, while the information on manufacturing tolerances and various technical requirements is only treated as annotation information. When performing capp, it is often necessary to re-do the part information. Input (including geometric features). This not only wastes a lot of manpower and material resources for repeated labor, but also is not conducive to the feedback of capp to the cad system for manufacturability evaluation, to achieve the purpose of optimizing product design. 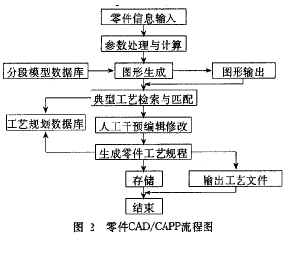
Research on cad/capp integration technology based on feature design (Figure)
