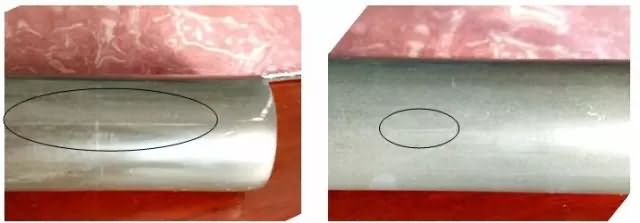
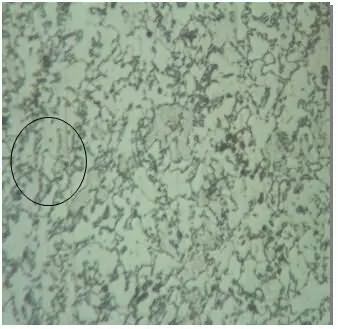
A batch of Φ21.66 wire, material grade 20MnTiB, production grade M12 10.9 fishtail bolt, the product cracking phenomenon was found during the production process. After a series of tests and analysis, not only the material segregation and hairline were found in the raw materials, but also in the series of test analysis, the crack propagation and extension of the product after heat treatment was explained, and the proportion of cracked products increased. The reason was not only the raw materials themselves. In addition, it is closely related to the heat treatment process. Status of production of fishtail bolts 1. Technical conditions of the product: The diameter of Φ16.88mm wire is used, and the M24 10.9 fishtail bolt is produced by cold head forming method. 2. Production process: After the material is formed by cold heading, the blank is rolled, and the finished product is sent to the heat treatment company for surface carburizing and quenching. 3, after the heat treatment inspection, found that the product cracked seriously (Figure 1 red box crack); Figure 1 left crack developed from the head to the neck, throughout the head; Figure 1 right, in the crack in the rod The neck joint extends to the position of the rod, and the total length of the crack reaches 3 cm or more. The thread below the head presents an arbitrary, curved arc state; in Figure 1, the crack increases the length of the crack than the raw material. Wire condition The cracking of the fishtail bolts has seriously affected the quality of the company's products and the credibility of the company. It is necessary to trace the source and find out the root cause of the fracture. According to the production statistics of the quality assurance department, in the semi-products after the cold heading process, the crack ratio was found to be 5%-6%. After the materials were selected, some products were cracked after heat treatment, and the two products were cracked. The total number exceeds 10% of the total number of products, causing high concern. First check the actual condition of the production of the first wire and wire, as the first basis for discovering and judging the root cause of the crack. Some materials were found to be cracked on the shop floor (see Figure 2). First, the wire condition Figure 2 Crack condition of the wire From the actual situation of the wire, there are obvious cracks on the surface of the wire. These cracks are tiny cracks—the type of hairline. The length and depth of the hairline are different from the left side of Figure 2; the crack is very obvious on the left side of Figure 2. There is a certain depth, the length of the hairline reaches 5CM, the figure 2 is right, the hairline is relatively shallow, the length is also short, but the length also reaches about 2CM. The appearance of these cracks seriously affects the quality of the product. The cracks of different sizes and different depths are found in the product cuttings. According to the statistics of the quality department, the ratio of crack blanks to more than 5% of the total amount is generated. As can be seen from Figure 2 above, without cold cuts, these cracks are produced in the raw materials. In order to further examine the causes and analyze the cracks, we conducted various tests on materials, semi-finished products, and heat-treated products. 1, hardness test: (1) Raw material hardness: The hardness of raw materials is in the range of HRB85.6-HRB88.7, and the average value is HRB87.1. According to the technical requirements of raw materials, the hardness is controlled within the range of ≦HRB90. Although the hardness of the material is too high, the difficulty of cold heading is increased, but within the requirements. , to meet technical requirements. (2) Hardness after heat treatment: The hardness of the bolt after heat treatment, whether it is broken bolt or normal bolt, is in the range of HRC33-HRC36.9, which meets the technical requirements of 10.9 high-strength bolt HRC32-HRC39. Hardness is the appearance of performance and must be further analyzed. 2. Chemical composition analysis: After spectral analysis, the content of each element of 20MnTiB is within the technical requirements. 3, crack detection: Figure 3 Shape of raw material crack 100X Metallographic sample testing was carried out on cracked raw materials. Fig. 3 left, cracked raw material crack (opening width: 41.47 μm, opening depth: 25.73 μm); Fig. 3 right, cracked raw material crack (opening: 37.27 μm, depth: 44.52 Îœm), the width and depth of cracks are different; however, the cracking of these raw materials increases the possibility of expanding cracks in cold heading, affects product quality, and increases the risk of heat treatment and crack propagation. 4. Annealed tissue: The state of 20MnTiB material entering the company is annealed. We made the metallographic sample and observed its microstructure (see Figure 4). Figure 4 Raw material annealing organization 100X According to the metallographic picture of the annealed structure, the state of the structure is pearlite + ferrite, and the distribution of most of the regional tissues is relatively uniform, and there is no state in which the normal and large ferrites are concentrated. In general, the metallographic structure belongs to Qualified and acceptable organizational form; however, some areas (the inner part of the black circle in the metallographic picture) have segregation of carbide concentration. If these carbide structures are concentrated on the surface of the product, the carbide will affect to a certain extent. The deformation of the product and the relatively large deformation area are prone to cracking, which is one of the causes of crack formation and must be taken seriously. 5. Quenching and tempering tissue testing: Figure 5 bolt heat treatment and tempering organization 500X According to the national standard, GB/T13320 "steel die forging metallographic organization rating map" rating standard, the gap organization is: tempered sorbite + ferrite, the organization is relatively small, rated as quenching organization level 2, belonging to Normally qualified metallographic organization. The left picture shows the metallographic picture of the cracked product. The microstructure of the normal bolt is slightly worse than that of the normal bolt on the right. The metallographic structure of the normal bolt on the right side is more evenly distributed and the structure is better. 6. The condition of the crack after heat treatment: Figure 6 crack after heat treatment 500X During the heat treatment process, thermal stress and tissue stress are greatly increased due to the process of heating and cooling, which increases the risk of cracking of the product, especially the crack in the material may expand or even break, whether the product is cracked or not. It is still not allowed to exist because the bolt is broken. The crack opening in Fig. 6 is the condition after heat treatment. The crack after heat treatment is larger than the crack in the material. The opening width of the crack is 129.51 μm, which is more than three times the original crack width of 41.47 μm; the depth of the crack reaches: 109.47 μm. It is about 4 times the original crack depth of 25.73 μm. Moreover, at the lower end of the notch, new cracks appear under the original crack, which is evidence of the thread expansion caused by the heat treatment; the thread after heat treatment, compared with the initial crack, regardless of the length, width and shape, Larger changes, which are thermal strains due to thermal stress after heat treatment, promote crack propagation and growth, which is significantly related to the improper selection of heat treatment processes. Analysis of the causes of cracks 1. Initial crack: There is an initial crack in the material. It can be seen from the macro photograph in Fig. 2 that both the left and right images have cracks in the raw materials, and the crack size and depth are different (Fig. 3 metallographic crack photo), both of which are straight lines. form. 2. After testing, the hardness of the material is within the required range, the chemical composition of the material reaches the technical standard, the quality of the material, and the annealed structure meet the standard requirements. 3. Crack propagation: The initial crack is extended during the heat treatment process (Fig. 6). It can be seen from Fig. 1 that the surface of the head flange is straight, which is the shape of the original thread. The shape of the crack below the neck begins to change, which is an irregular crack. The shape is an irregular arc, the length of the thread increases, and the crack is always cracked to the stem of the bolt. It can be seen that the crack is the original cracked hairline that begins to grow and develop. After the heat treatment, a relatively long crack is formed from the head to the stem. The length of the crack is continuously increased and expanded compared with the original hairline. 4. Improper carburizing heat treatment process: The 20MnTiB material is used to produce 10.9 high strength bolts for carburizing and quenching. However, in the carburizing and quenching process, the quality of the quenching and tempering is not in place due to the selection or improper arrangement of the process, which in turn causes cracking. 1) Improper carburizing process: It can be seen from the following figure 8 that the thickness of the carburized layer is not uniform, the carburizing layer is deep in some areas, and the carburizing layer is shallow in some areas; in the surface range of less than 150 μm in the picture, Figure 8 The carburized layer on the upper left is 70.91μm, while the carburized layer close to the lower part reaches 106.70μm. It can be seen that the infiltration layer is extremely uneven, which is caused by the improper selection of the parameters of the carburizing process. 2), quenching stress is large: the head of the fishtail bolt in Figure 7 is cracked, the shape of the crack is: irregular arc, the arc is arbitrary, irregular shape, shape and fastener surface defect, bolt quenching crack The narrative is similar (see GB/T5779 standard for details). 3), the uneven layer is reflected in the carburizing process, to increase the temperature instead of carburizing time, the thickness of the layer is thick and uneven, increasing the internal thermal stress; at the same time, after carburizing, pre-cooling time, When the pre-cooling temperature is not in place, quenching is performed, so that the irregular stress arc is generated by thermal stress→thermal strain→cracking, which is caused by improper selection of the heat treatment process parameters, and is the main cause of quenching cracks. Cracks are always the weakest part of the material, and cracks are easily generated on the surface or defects of the bolt. Inclusions, segregation or second phase particles in the interior of the material tend to accumulate at the defects, resulting in stress concentration, which may develop and transform into strain, which leads to the initiation of cracks. Once a crack is generated, it will continue to develop and expand in various processes. If the heat treatment and quenching process of the fasteners is proper, the microstructure can be improved; conversely, improper heat treatment and tempering will promote the development of micro defects. There are two reasons for the cracking of the fishtail bolt: Author: Yan Zhen of China Fastener Info consultants, Shanghai Detroit Precision Fastener Co., Ltd. metallurgical engineer Minister Cheng Ping Wang Huawei warranty. On July 28th, 2016, the topic “The influence of alloying elements and inclusions on high-strength fastenersâ€, which was lectured by senior expert Mr. Zhen Zhenzhong, will be held in Hangzhou. It is worth looking forward to!
An angle grinder, also known as a side grinder or disc grinder, is a handheld power Tool used for grinding (abrasive cutting) and polishing. Although developed originally as tools for rigid abrasive discs, the availability of an interchangeable power source has encouraged their use with a wide variety of cutters and attachments.
Angle grinders can be powered by an electric motor or compressed air. The motor drives a geared head at a right-angle on which is mounted an abrasive disc or a thinner cut-off disc, either of which can be replaced when worn. Angle grinders typically have an adjustable guard and a side-handle for two-handed operation. Certain angle grinders, depending on their speed range, can be used as sanders, employing a sanding disc with a backing pad or disc. The backing system is typically made of hard plastic, phenolic resin, or medium-hard rubber depending on the amount of flexibility desired.
Electric Angle Grinder,lithium electric tool Behappy Crafts (suzhou)Co.,Ltd , https://www.jshaoyue.com
Second, the detection status: 




in conclusion:
Internal factors: material segregation and hairline are the primary causes of cracks; external factors: carburizing heat treatment process is not in place, is the pusher to increase cracks. 
The fish tail bolt cracked. Where is the problem?
